










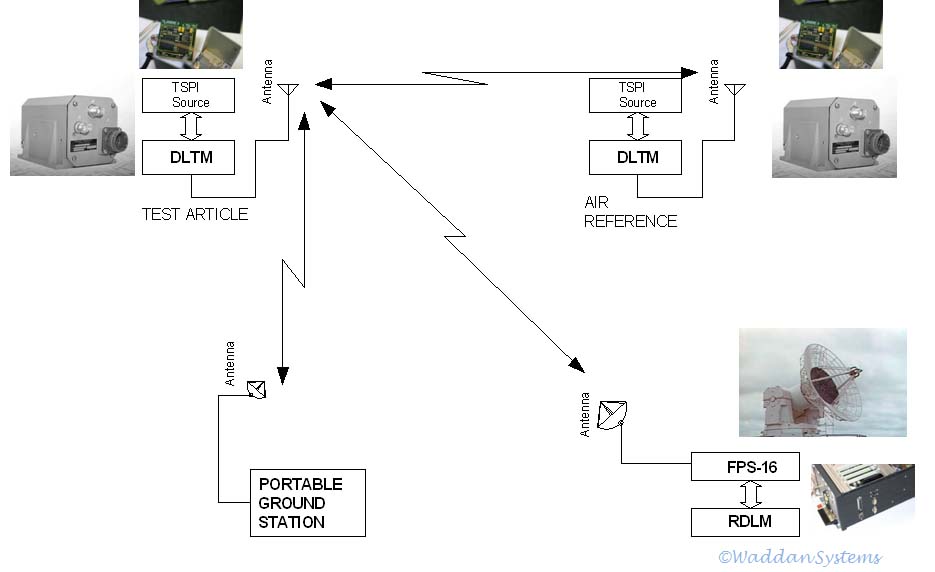
 The
TSPIGII Transponder Data Link illustrated in the above diagram employs
Waddan TSPIGII (for position and heading of an airborne test article)
and an efficient radio shown on the left. Early experiments used parts
of a C-Band transponder as the analog front end of the data link to
communicate with an FPS-16 radar (from Apollo era). The radar loop was
temporarily modified using a CompactPCI based Radar Data Link Module
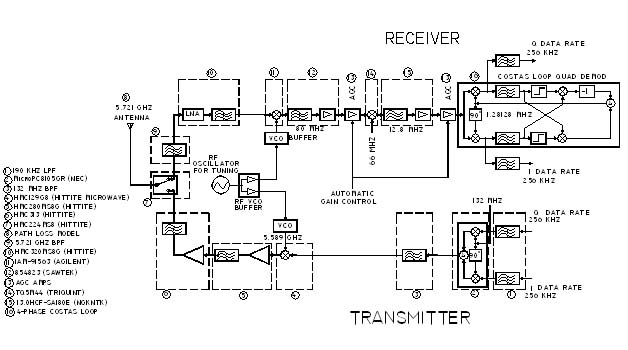
(RDLM). The digital partition of the DLTM is implemented using Xilinx
FPAGA as the core. TTDL can use either QPSK or GMSK data modulation
scheme. The data rate required for TSPI transmittal is 256 k bits per
second, and the bandwidth is 2 MHz With a little creativity the TTDL
can be used for telemetry over ranges as long as 500 miles.
The
TSPIGII Transponder Data Link illustrated in the above diagram employs
Waddan TSPIGII (for position and heading of an airborne test article)
and an efficient radio shown on the left. Early experiments used parts
of a C-Band transponder as the analog front end of the data link to
communicate with an FPS-16 radar (from Apollo era). The radar loop was
temporarily modified using a CompactPCI based Radar Data Link Module
(RDLM). The digital partition of the DLTM is implemented using Xilinx
FPAGA as the core. TTDL can use either QPSK or GMSK data modulation
scheme. The data rate required for TSPI transmittal is 256 k bits per
second, and the bandwidth is 2 MHz With a little creativity the TTDL
can be used for telemetry over ranges as long as 500 miles.
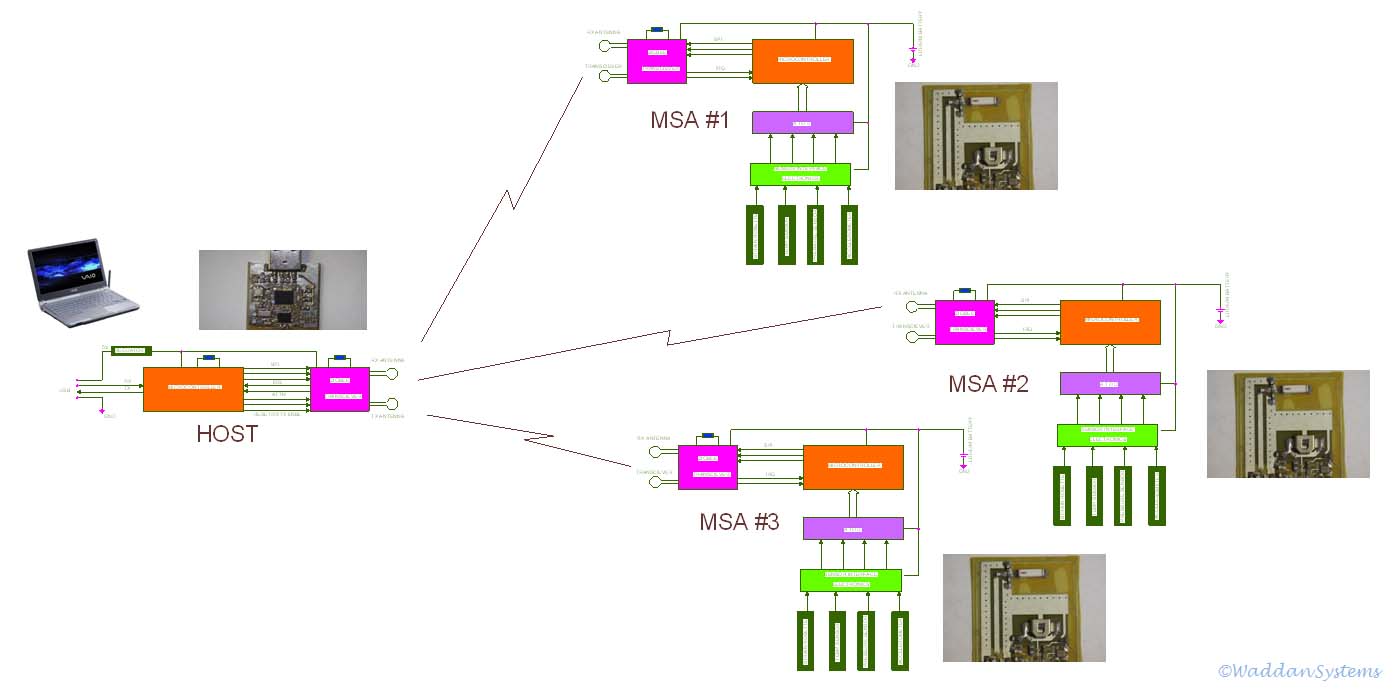 The Aircraft Nodal Data Acquisition System (ANDAS) is based upon the
short haul ZigBee networking standard. It employs a number of thin
microminiature sensor assemblies (MSAs) and a USB Host module. The MSAs
are cemented for test measurements at several key locations (nodes) on
a complex structure such as an aircraft. (Since the MSA has to be
cemented on a smooth surface, all electronics components are placed on
one side of the flex board). When prompted by the Host, they collect
the measurement data, and transmit it to the Host. An MSA incorporates
an integrated sensor (capable of measuring acceleration, pressure,
temperature and surface strains), a microcontroller, a ZigBee
transceiver and a battery for power. A power management scheme
minimizes the use of the battery, thus, prolonging its life
significantly. The Host module also incorporates a microcontroller and
a ZigBee transceiver. At the current state of firmware development, an
ANDAS cluster consists of a Host interacting with up to 16 MSAs with 30
Hz data update rate.
The Aircraft Nodal Data Acquisition System (ANDAS) is based upon the
short haul ZigBee networking standard. It employs a number of thin
microminiature sensor assemblies (MSAs) and a USB Host module. The MSAs
are cemented for test measurements at several key locations (nodes) on
a complex structure such as an aircraft. (Since the MSA has to be
cemented on a smooth surface, all electronics components are placed on
one side of the flex board). When prompted by the Host, they collect
the measurement data, and transmit it to the Host. An MSA incorporates
an integrated sensor (capable of measuring acceleration, pressure,
temperature and surface strains), a microcontroller, a ZigBee
transceiver and a battery for power. A power management scheme
minimizes the use of the battery, thus, prolonging its life
significantly. The Host module also incorporates a microcontroller and
a ZigBee transceiver. At the current state of firmware development, an
ANDAS cluster consists of a Host interacting with up to 16 MSAs with 30
Hz data update rate.
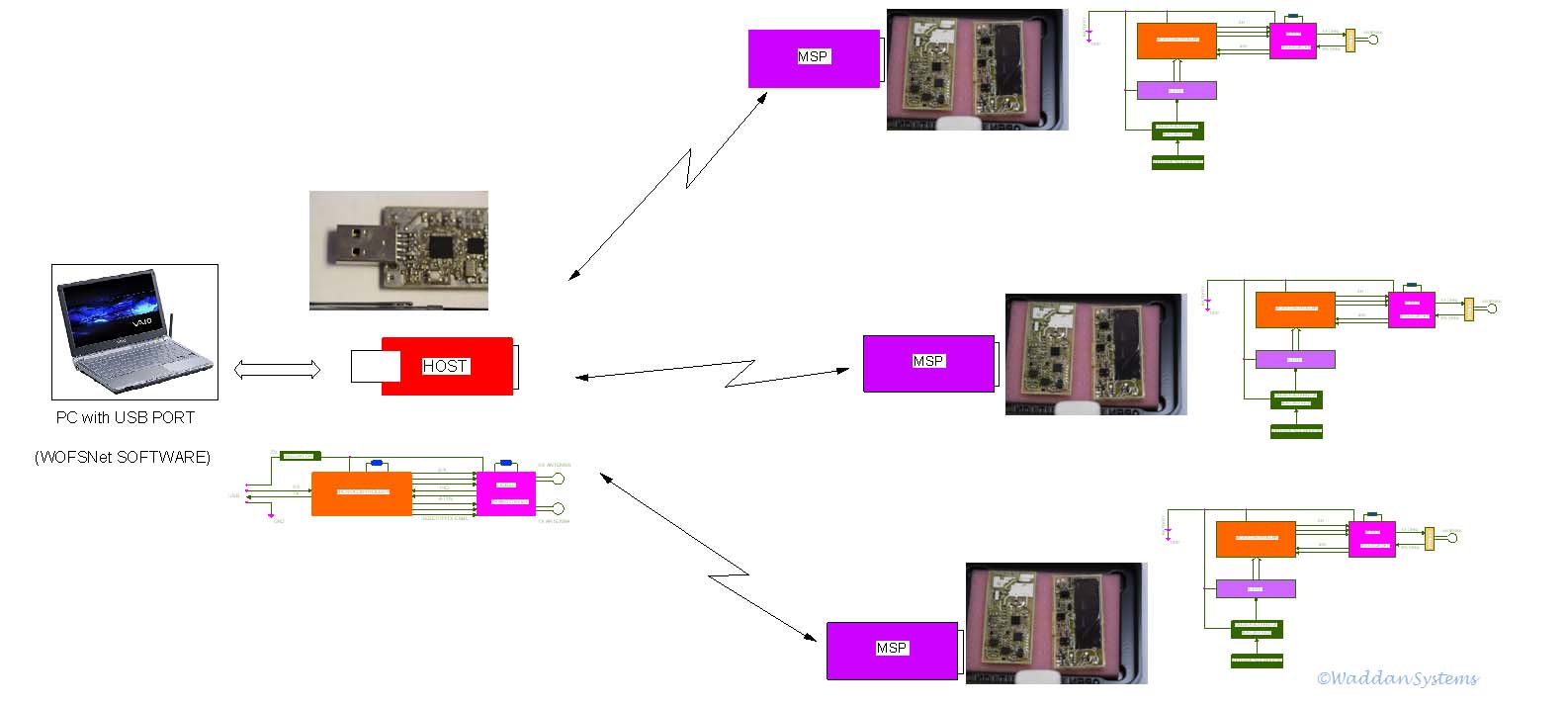 The wireless design of this system is similar to that of
ANDAS with one slight hardware improvement. The Zigbee transceiver
function has also been merged in the microcontroller chip. The
sensor partition is also modified to accommodate the porous optical gas sensing function.
For higher sensitivity, the chip uses a spread-out waveguide sensing area.
The wireless design of this system is similar to that of
ANDAS with one slight hardware improvement. The Zigbee transceiver
function has also been merged in the microcontroller chip. The
sensor partition is also modified to accommodate the porous optical gas sensing function.
For higher sensitivity, the chip uses a spread-out waveguide sensing area.
