










Test station software generally has two components. The first part controls the test station and the second part is used to apply a stimulus to the article under test and register the response. The automated test station can perform tests under hundreds of configuration, and save thousands of output data samples. Examples of this type of software can be found with:
Rate Table control test station where gyros, IMUs and entire navigation systems can be tested

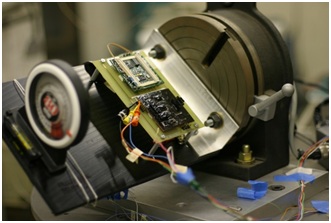
Dividing Head Control test station where an accelerometer can be subjected to a component of gravitational acceleration to measure its response
Methane Gas Testing Station where a gas sensor is immersed in a mixture of methane and nitrogen, and sensor response is registered in incremental time steps
